1. Introduction
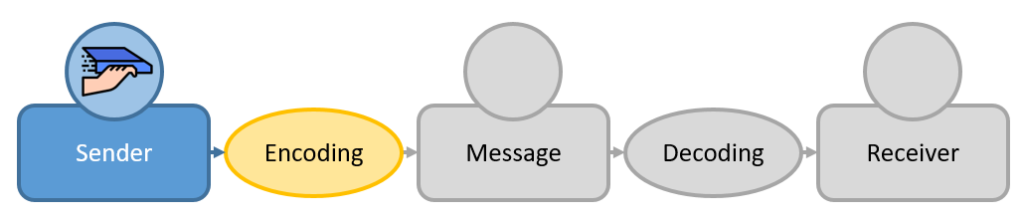
The communication process is the process of passing information from one person to another. It can be as simple as passing a note in class, or as complicated as giving a presentation to a group of people. The process is made up of five main parts: sender, message, receiver, feedback, and noise..

1. Sender
sender is the person who initiates the communication process by creating and sending a message. The sender is responsible for ensuring that the message is clear and understandable, and that it is received by the intended recipient. The sender must also be able to effectively encode the message, which involves choosing the appropriate words and symbols to convey the desired meaning.
The sender is the starting point of the communication process, and as such, plays a crucial role in ensuring its success. Effective communication requires that the sender be clear about what they want to communicate, and be able to effectively encode the message. If the sender is unclear about the message they want to communicate, or if they are unable to effectively encode it, the communication process is likely to break down.
It is also important for the sender to be aware of the receiver’s needs and preferences. If the sender does not take the receiver’s needs into account, the message may not be properly understood. In addition, the sender must be careful not to send a message that is too complex or too simple for the receiver. If the message is too complex, the receiver may have difficulty understanding it. If the message is too simple, the receiver may feel that the sender is not taking their needs into account.
A sender can have one of several roles in the communication process:
- Communicator: The sender might need to inform another party about something or delegate a task
- Investigator: The sender might need to find out some information from another party
- Assessor: The sender might need to access/test how well the other party is informed
2. message
message is the content that is communicated. It is the information that is conveyed by the sender to the receiver. The message can be in the form of spoken words, written words, or nonverbal communication.
The message is the most important part of the communication process because it is the reason for the communication. The message must be clear and concise so that the receiver can understand it. The message must also be relevant to the receiver.

The sender must encode the message into a form that can be understood by the receiver. The receiver must then decode the message and interpret it based on their own understanding.
The message can be affected by the channel through which it is sent. The channel is the medium through which the message is transmitted. The channel can be direct, such as face-to-face communication, or indirect, such as email.
The message can also be affected by the context in which it is communicated. The context is the situation in which the communication takes place. The context can include the physical environment, the social environment, the relationship between the sender and receiver, and the purpose of the communication.
3. Receiver & Feedback
receiver is just as important as that of the sender. The receiver is the one who interprets the message that the sender is trying to communicate. This means that the receiver must be actively engaged in the communication process in order to ensure that the message is interpreted correctly.
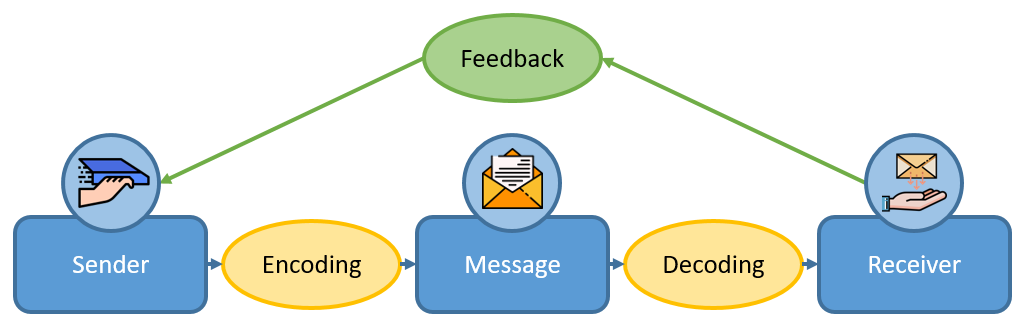
One of the most important things that the receiver can do is to provide feedback to the sender. This feedback can be either verbal or nonverbal.
- Verbal feedback is when the receiver responds to the sender’s message with words.
- Nonverbal feedback is when the receiver responds with body language, such as facial expressions or gestures.
Feedback is important because it lets the sender know that the receiver is understanding the message. It also allows the sender to know if the receiver needs more information or clarification.
One of the most important feedback techniques is to ask questions. This is especially important when the receiver is not sure what the sender is trying to communicate. By asking questions, the receiver can get a better understanding of the message. Asking questions can also help to clarify any misunderstandings.
The receiver also needs to be aware of the context of the communication. This includes the situation, the relationship between the sender and receiver, and any other factors that might affect the interpretation of the message. For example, if the receiver is in a hurry, they might not have the time to fully process the message. Or, if the receiver is tired, they might not be able to pay attention to the message. Context is important because it can help the receiver to understand the message better.
Finally, the receiver needs to be honest with the sender. This means that the receiver should not try to interpret the message in a way that is convenient for them. Instead, the receiver should try to understand the message the way that the sender intended. This can be difficult, but it is important in order to ensure that the communication is effective.
4. Noise
Noise is an important factor to consider in the human communication process. It can be defined as any distractions that impede effective communication. Noise can create communication barriers by causing misunderstandings and preventing effective communication.
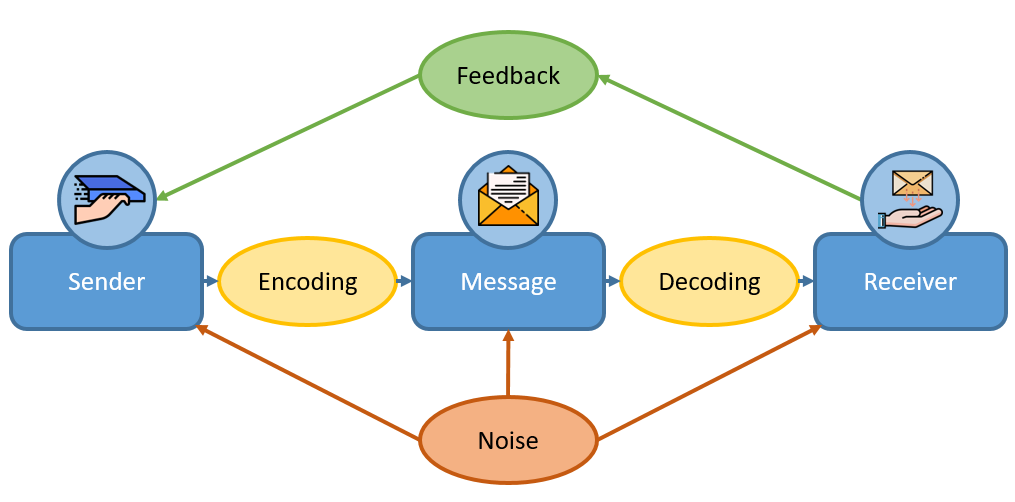
The first step to reducing the effects of noise on communication is to be aware of the different types of noise and the ways that they can interfere with communication. Once we are aware of the types of noise, we can then take steps to reduce or eliminate them.
There are two main types of noise: physical and psychological:
Psychological noise is created by our own thoughts, emotions, and attitudes. It can include things like worry, stress, or self-doubt.
Physical noise is any type of distraction that originates from our physical environment. This can include things like loud music, disruptive conversations, or ambient noise.
One way to reduce physical noise is to create a physically quiet environment. This can be done by turning off any sources of noise, such as music or television, and by asking others to be quiet. If we are in a public place, we can try to move to a quieter location. Another way to reduce physical noise is to use noise-cancelling headphones or earplugs.
We can reduce psychological noise by taking time to relax and clear our minds before communicating. We can also try to reduce the amount of distractions we have around us. If we are feeling stressed or anxious, we can take a few deep breaths and focus on the present moment. We can also try to reframe our thoughts in a more positive light.
The last step to reducing noise in communication is to be patient and understanding. We all have different communication styles and preferences. We can’t expect others to change their communication style to match our own. Instead, we need to be patient and understand that not everyone communicates in the same way. We also need to be willing to compromise and adapt our own communication style to meet the needs of the situation.
